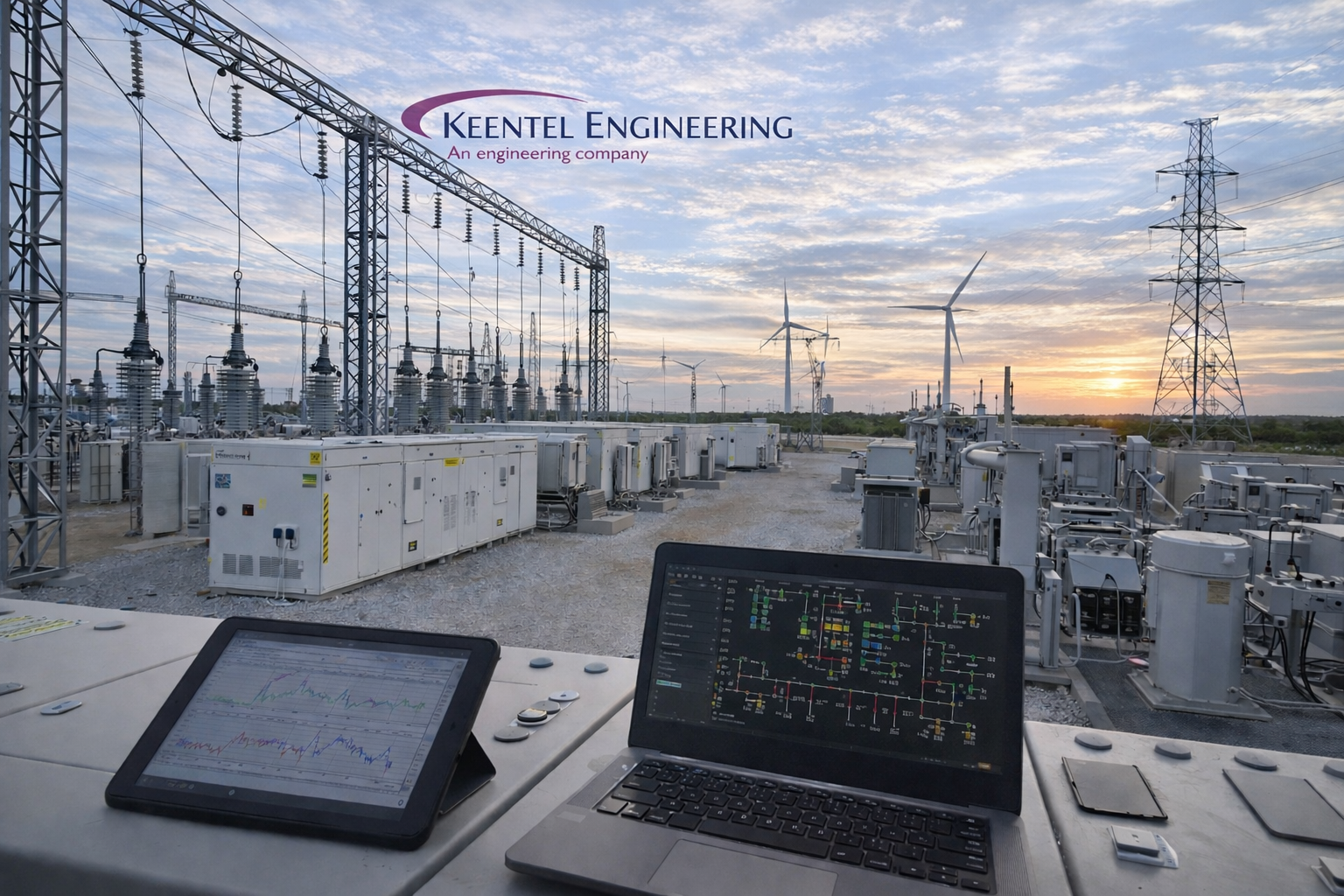
A Coordinated Electric System Interconnection Review—the utility’s deep-dive on technical and cost impacts of your project.
Challenge: Frequent false tripping using conventional electromechanical relays
Solution: SEL-487E integration with multi-terminal differential protection and dynamic inrush restraint
Result: 90% reduction in false trips, saving over $250,000 in downtime
Engineering Specifications for High-Voltage Gas-Insulated Substations (GIS) per IEEE Std C37.123-2023
July 18, 2025 | Blog
Introduction
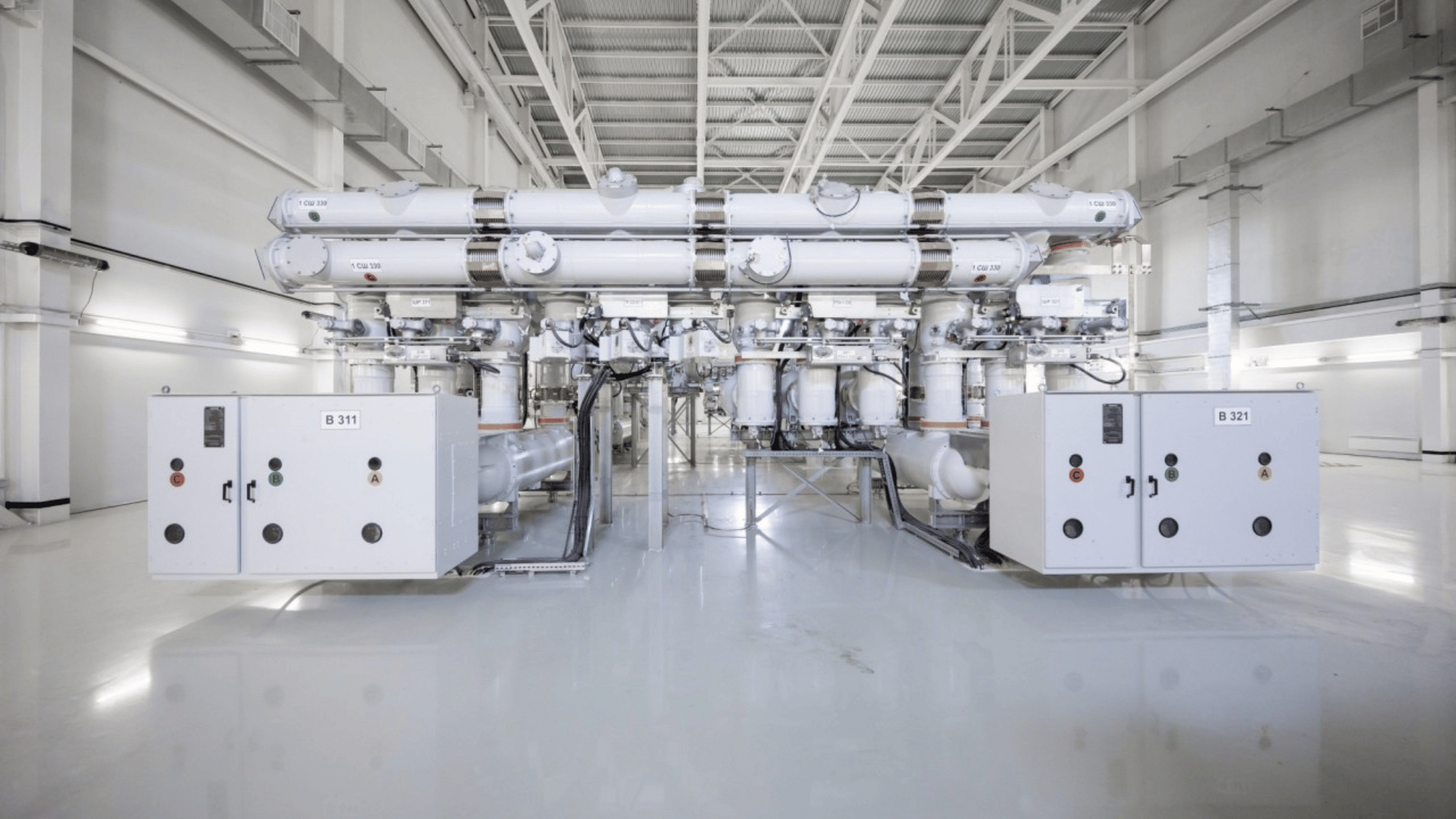
High-voltage Gas-Insulated Substations (GIS) are essential in modern power systems where compactness, reliability, and safety are critical. The IEEE Std C37.123-2023 provides a comprehensive framework for specifying GIS installations rated 52 kV and above. At Keentel Engineering, we help utilities and EPC firms translate this standard into actionable specifications that improve design quality, ensure compliance, and streamline procurement.
This guide covers the essential clauses, technical requirements, and best practices that engineers must consider when specifying GIS systems based on IEEE C37.123-2023.
Scope and Intent of IEEE C37.123-2023
The IEEE Std C37.123-2023 serves as a guide to develop procurement specifications for GIS rated above 52 kV. It focuses on the technical components and omits commercial terms. It supports engineers in drafting requirements for design, fabrication, testing, installation, and in-service performance.
Specification Format Structure
Clause 1.5 outlines a structured approach to GIS specifications, including:
- One-line diagrams
- Environmental and service conditions
- GIS component details
- Interfaces and responsibilities
- Test procedures and documentation
Keentel Engineering integrates these clauses into detailed project-specific templates for utilities.
Standards and References Used
Clause 2 lists essential IEEE, IEC, ASTM, and NEMA references. Key among them are:
- IEEE C57.13 for instrument transformers
- IEEE C37.017 for bushings
- IEC 62271-209 for cable terminations
We recommend including these in your reference list for any GIS procurement document.
Required Service Conditions
Clause 4 emphasizes environmental data including:
- Altitude
- Pollution levels
- Seismic category (IEEE Std 693 compliance)
Accurate site condition data influences GIS insulation levels, enclosure design, and structural interfaces.
What Is the Scope of Supply? (Clauses 5.1–5.3)
Divide responsibilities clearly between supplier and user. Typical user-furnished items include foundations, conduit, SCADA systems, and erection labor. Suppliers provide:
- Circuit breakers, disconnects, ground switches
- Enclosures, bushings, control cabinets
- Insulating gas and accessories
- Site services and test reports
Keentel project scopes include annotated diagrams like Figure 1 of the standard for visual clarity.
Proposal Requirements
Suppliers must provide:
- Drawings: one-line, general layout, gas schematic
- Gas handling procedures
- Ratings, dimensions, and weights
- Seismic calculations
- Spare parts and special tools list
Use Annex B to streamline bid evaluations across multiple vendors.
GIS Design Considerations
Clause 7 highlights critical design elements
- Interlocks (electrical/mechanical)
- Expansion joints and bolted connections
- External enclosures and corrosion protection
- Grounding per IEEE Std 80
- Wiring shielding and protection
Design details must comply with IEEE C37.122.1 and should factor in maintenance access, thermal cycling, and electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Component-Level Requirements
Each major GIS component has specific requirements:
- Circuit Breakers: Comply with IEEE C37.04 and C37.09 for dielectric, thermal, and interrupting duties
- Disconnects & Grounding Switches: Visual indicators, interlocks, and fail-safe mechanisms
- Gas System: Pressure zones, density monitoring, SF6 or alternative gases
- Instrument Transformers: Shorting terminal blocks, accessible secondary testing
- Bushings & Terminations: Mechanical strength, creepage distances, proper flanging
We encourage using Annex A tables to itemize component specs.
Testing Requirements
Testing is split into:
- Design Tests: Type tests like dielectric, temperature rise, and arc withstand
- Routine Tests: Mechanical operations, insulation checks, leak tests
- Factory Acceptance Tests (FATs): In presence of the user
- Field Tests: Gas quality, interlocks, continuity, and HV withstand
Keentel’s FAT and commissioning checklists align directly with Clause 9.
Documentation and Quality Assurance Are Required
Quality assurance is anchored in ISO 9001. Required documents include:
- Seismic and structural calculations
- Grounding study
- Operation manuals
- Mimic diagrams and nameplates
Use Annex A for specifying project parameters and Annex B for collecting uniform bid data.
Conclusion
IEEE C37.123-2023 is a vital resource for high-voltage GIS engineering. It offers structure, rigor, and clarity for developing specifications that enhance GIS performance and lifecycle reliability. At Keentel Engineering, we incorporate this guide into our project workflows to ensure code compliance, technical excellence, and project success.
FAQs on IEEE C37.123-2023 for Engineers
To support engineers, utility planners, and substation designers, we've compiled this list of frequently asked technical questions based on the IEEE C37.123-2023 standard for Gas-Insulated Substations (GIS). These answers reflect Keentel Engineering’s application of the standard in GIS procurement and design.
1. What is the IEEE C37.123-2023 standard?
It is a guide for specifying high-voltage GIS systems rated 52 kV and above, focused on technical and performance parameters only.
2. Does IEEE C37.123-2023 apply to turnkey project specifications?
No, the standard addresses technical, not commercial or turnkey aspects.
3. What insulating gases are covered in the standard?
Primarily SF6, but it also references alternative gases compliant with IEC 60376 and 60480.
4. Is this standard harmonized with IEEE C37.122?
Yes, it aligns closely with IEEE C37.122 and C37.122.1 for consistency in GIS design practices.
5. What is the purpose of Annex A in IEEE C37.123-2023?
To capture site-specific service conditions, including environmental, electrical, and structural design inputs.
6. What is Annex B used for?
Annex B provides a uniform format for proposal data—ideal for comparing vendor bids efficiently.
7. Are visual disconnects required for GIS systems?
Yes, Clause 8 requires visual indicators for contact position verification as a best practice.
8. What defines acceptable GIS insulation levels?
Levels must comply with IEEE C37.122, including BIL (Basic Insulation Level), SIL, and power-frequency withstand.
9. How should grounding be specified?
Grounding systems must follow IEEE Std 80 and C37.122.1, accounting for touch/step voltages and system faults.
Learn how we assist with grounding studies
10. Are Factory Acceptance Tests (FATs) mandatory?
Yes, at least one representative bay must undergo FATs in the presence of the user per Clause 9.3.
11. What is the minimum mechanical endurance requirement for circuit breakers?
Circuit breakers must support at least 1,000 mechanical operations.
13. How many gas zones are recommended?
At minimum: one gas zone per circuit breaker, VT, and surge arrester. Larger GIS setups may require more.
14. What are the acceptable leakage rates for GIS enclosures?
Per IEEE C37.122; however, some U.S. states may require lower GWP (Global Warming Potential) compliance.
15. What is the preferred method of enclosure construction?
Bolted and gasketed joints are recommended. Field welding is discouraged unless explicitly required.
16. Does the standard address seismic compliance?
Yes, GIS installations must conform to IEEE Std 693 for seismic qualification and structural stability.
18. Can platform access and overhead crane support be customized?
Yes, Clause 5 allows users to specify working clearances, access platforms, and crane integration.
19. What GIS field tests are required?
Leak detection, gas purity validation, interlock testing, and low-frequency withstand tests.
20. Are partial discharge (PD) tests required under IEEE C37.123-2023?
Optional, but recommended if PD sensors are integrated in GIS components.
21. What are common transformer connection issues during GIS integration?
Issues include flange misalignment, vibration damping, and gas barrier inconsistencies.
22. How should auxiliary systems be specified in GIS design?
Include heaters, lighting fixtures, and receptacles as outlined in Clause 8.12.2.
23. Can Bay Control Units (BCUs) include protection functions?
Yes, if specified, BCUs may combine protection and control functionalities.
24. What file formats are expected for GIS proposal drawings?
CAD-compatible formats with dimensional layouts, load data, and 3D modeling views are standard.
25. Where can I get help applying IEEE C37.123-2023 in my project?
Ready to Build Your Next GIS Project to IEEE Standards?
Contact Keentel Engineering for expert guidance on substation engineering, GIS specifications, and compliance support.

About the Author:
Sonny Patel P.E. EC
IEEE Senior Member
In 1995, Sandip (Sonny) R. Patel earned his Electrical Engineering degree from the University of Illinois, specializing in Electrical Engineering . But degrees don’t build legacies—action does. For three decades, he’s been shaping the future of engineering, not just as a licensed Professional Engineer across multiple states (Florida, California, New York, West Virginia, and Minnesota), but as a doer. A builder. A leader. Not just an engineer. A Licensed Electrical Contractor in Florida with an Unlimited EC license. Not just an executive. The founder and CEO of KEENTEL LLC—where expertise meets execution. Three decades. Multiple states. Endless impact.
Services

Let's Discuss Your Project
Let's book a call to discuss your electrical engineering project that we can help you with.

About the Author:
Sonny Patel P.E. EC
IEEE Senior Member
In 1995, Sandip (Sonny) R. Patel earned his Electrical Engineering degree from the University of Illinois, specializing in Electrical Engineering . But degrees don’t build legacies—action does. For three decades, he’s been shaping the future of engineering, not just as a licensed Professional Engineer across multiple states (Florida, California, New York, West Virginia, and Minnesota), but as a doer. A builder. A leader. Not just an engineer. A Licensed Electrical Contractor in Florida with an Unlimited EC license. Not just an executive. The founder and CEO of KEENTEL LLC—where expertise meets execution. Three decades. Multiple states. Endless impact.
Leave a Comment
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.